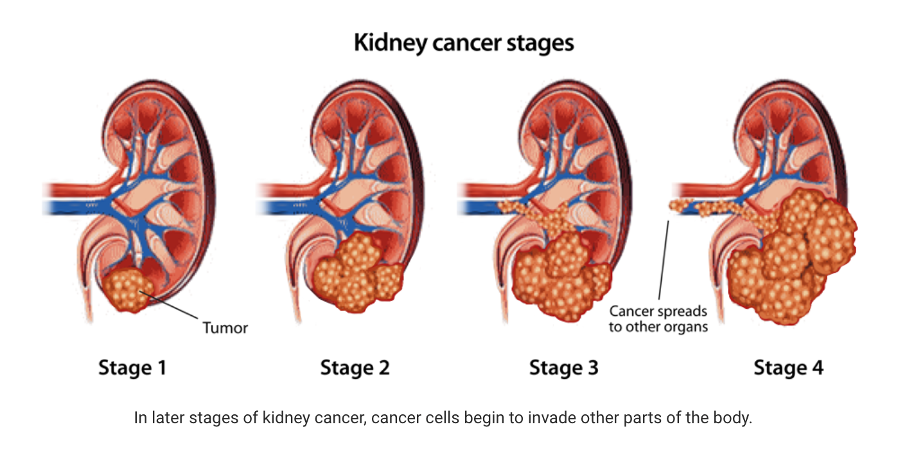
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), is one of the top ten most common cancers in the United States. It originates in the kidneys—two bean-shaped organs responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, and producing urine. Early diagnosis dramatically improves outcomes, making awareness essential.
There are both malignant and benign types of renal masses. Although small renal masses can harbor kidney cancer in 80% of cases, benign renal masses do occur in ~20%. This could include oncocytomas, angiomyolipomas, multilocular cystic nephromas, benign complex renal cysts, maong others.
The majority of these small renal masses are low grade malignancies. The average growth rate is 3-5 mm per year, although the range can be from 0-15mm per year. Masses less than 3 cm have a small likelihood of metastasis on presentation (<1%). After tumors exceed 3 cm this rate increases somewhat and might be as high as 5% in masses over 4 cm. If your tumor is <3cm, it may be reasonable to watch the tumor for interval growth.
| Risk Group | Stage | Stage Description | Modality | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Risk | Stage I | Tumor ≤7 cm, confined to kidney (T1a/T1b), N0, M0 |
- Physical Exam - Creatinine, eGFR - Ultrasound or CT |
Annually | Up to 5 years |
| Moderate Risk | Stage I–II | Tumor >7 cm but confined to kidney (T2), N0, M0 |
- Physical Exam - CBC, Creatinine, LFTs - CT abdomen/pelvis ± Chest X-ray |
Every 6 months × 2 years, then annually |
5–10 years |
| High Risk | Stage II–III | Tumor invades fat or major veins (T3) or local nodes involved (N1) |
- Physical Exam - CBC, Creatinine, LFTs - CT chest/abdomen/pelvis |
Every 3–6 months × 3 years, then every 6–12 months |
10 years or lifelong |
| Node-Positive or Metastatic | Stage III–IV | Node-positive (N1) or distant metastasis (M1) |
- Physical Exam - CBC, Creatinine, LFTs - CT/MRI chest/abdomen/pelvis |
Every 3 months × 2 years, then every 6 months × 3 years, then annually |
Lifelong |
| Active Surveillance | — | Small tumors <4 cm (T1a) in unfit or unwilling patients |
- Physical Exam - Labs - Renal US, CT, or MRI |
Every 3–6 months initially, then annually |
Ongoing |